Join us for conversations that inspire, recognize, and encourage innovation and best practices in the education profession.
Available on Apple Podcasts, Spotify, Google Podcasts, and more.
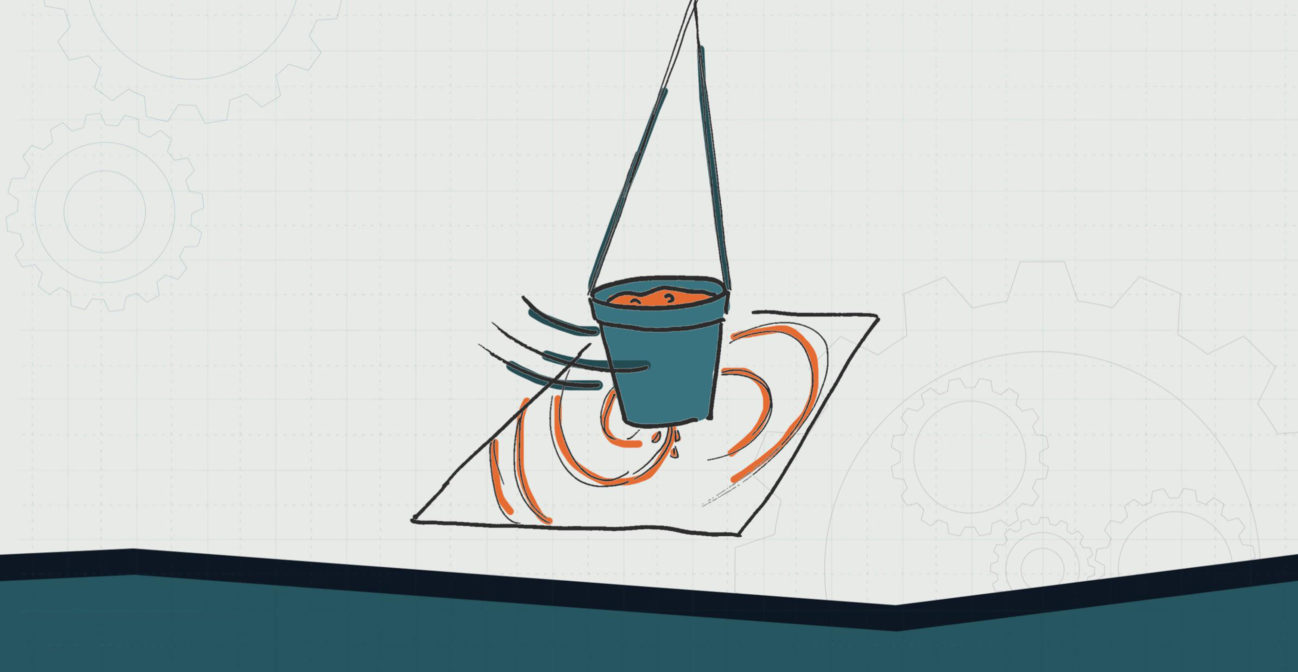
ELEMENTARY SCHOOL – LEVEL 3
The first scientific experiments on pendulums were conducted around 1602 A.D. by famous scientist Galileo Galilei. Until the 1900s, the pendulum was known as the world’s most reliable timekeeping technology. A pendulum is an object suspended from a point that can swing freely using the force of gravity. By creating a pendulum with a plastic cup, we can make gravitational art! This is a fun way for students to study gravity while getting a bit messy in the process, and what kid doesn’t love that?
MATERIALS NEEDED:
❏ Plastic cup or container
❏ String
❏ Pencil
❏ Tape
❏ 2 chairs
❏ Wooden dowels
DIRECTIONS:
OBJECTIVE: Student wills be able to predict future motion based on patterns from observations.
ESSENTIAL QUESTION(S):
NGSS CONNECTION:
3-PS2-2. Make observations and/or measurements of an object’s motion to provide evidence that a pattern can be used to predict future motion.
4-PS3-4. Apply scientific ideas to design, test, and refine a device that converts energy from one form to another.*
COMMON CORE CONNECTION:
ELA/Literacy
W.3.7 Conduct short research projects that build knowledge about a topic.
W.3.8 Recall information from experiences or gather information from print and digital sources; take brief notes on sources and sort evidence into provided categories.
SL.4.5 Add audio recordings and visual displays to presentations when appropriate to enhance the development of main ideas or themes.
W.4.7 Conduct short research projects that build knowledge through investigation of different aspects of a topic.
W.4.8 Recall relevant information from experiences or gather relevant information from print and digital sources; take notes and categorize information, and provide a list of sources.
4.OA.A.3 Solve multistep word problems posed with whole numbers and having whole-number answers using the four operations, including problems in which remainders must be interpreted. Represent these problems using equations with a letter standing for the unknown quantity. Assess the reasonableness of answers using mental computation and estimation strategies including rounding.
Mathematics
MP.4 Model with mathematics.
4.G.A.1 Draw points, lines, line segments, rays, angles (right, acute, obtuse), and perpendicular and parallel lines. Identify these in two-dimensional figures.
DOK:
Level 2: Concept
Level 3: Strategic Thinking