 |
The basics of atomic structure are as follows:
- Protons are positively charged particles, weighing 1 atomic mass unit (1.67x10-24 grams) and located in the nucleus.
- Neutrons are neutrally charged particles, weighing approximately 1 atomic mass unit and located in the nucleus.
Electrons are negatively charged particles weighing zero atomic mass units and located in the various orbitals of the energy levels outside the atomic nucleus. The electron actually weighs 9.11x10-28 grams. This means it would take about 1,830 electrons to equal the mass of one proton. Since the heaviest naturally occurring element has only 92 electrons in its normal state, we do not count the mass of the electrons in calculating the mass of the atom.
|
 |
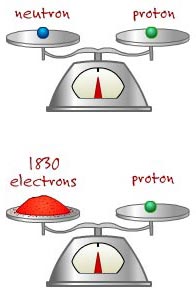
Almost all of the weight of an atom comes
from the protons and neutrons.
|
